
RapidSkills micro-credentials
The RapidSkills micro-credential programming offered through funding received from the province of Ontario’s Skills Development Fund has now concluded. The no-cost training took place between March 2022 and March 2023. At this time, we were unable to secure this funding for 2023-24. We’ll continue to explore possible training opportunities to meet the needs of the community.
Thank you to our participants and community partners who made the RapidSkills program a great success! If you have questions, comments, or are interested in exploring training options for your organization, please contact us.
About the RapidSkills program
Delivered in a fast and flexible format, RapidSkills micro-credentials included short-term, competency-based, industry-recognized certifications.
These micro-credentials were specific to the manufacturing sector and focused on key skill areas that had been identified as valuable by local manufacturing employers.

RapidSkills micro-certificates for the manufacturing sector
Each micro-certificate comprised up to five modules based on sectoral-focused feedback from regional stakeholders and employers.
Micro-credentials are designed to upskill workers in a part-time format. Digital badges were awarded for the completion of each micro-certificate module and for completion of the entire micro-credential.

Fundamental Shop Skills
Participants examined fundamental shop skills and learned to perform critical functions in this 30-hour module. Participated developed the skills to interpret engineering drawings, and examined manufacturing processes required to build components. They identified tolerances, materials and basic geometric dimensioning, as well as interpreted hidden lines, section lines, thread types and ground surface symbols.

Precision Machining
Participants learned to manufacture components using engineering drawings and traditional industrial machines. This three-module, 90-hour micro-certificate prepared participants for careers as material handlers, conventional mill and lathe machine operators, general machinists, tool and die makers, and mould makers.

Precision Machining module 1:
Hand, Bench and Layout Tools
Participants learned to read engineering drawings and, using precision measuring equipment, lay out the workpiece according to specified tolerances. Participants used height gauges, surface plates, angle plates, and protractors, along with the digital read out (DRO) on a vertical milling machine, to drill, tap and ream holes properly and safely.

Precision Machining module 2:
Conventional Vertical Milling Mach.
Participants learned to operate a vertical milling machine safely, and use tooling along with digital read outs to set X, Y and Z axis coordinates. Participants used cutting tools, including carbide cutters, to complete projects within working tolerances. Participants used mills and surface grinders to square up inserts.

Precision Machining module 3:
Conventional Lathe
Participants learned to set up and operate conventional metal cutting lathes safely. They learned how to turn diameters to lengths, bore holes, and make threading tools, to cut unified national fine and coarse threads. Participants built projects to engineering standards and tolerances. Speeds and feeds were covered, ensuring the best possible surface finish.

CNC
Participants explored CNC fundamentals using industry-grade tools and equipment in manufacturing. This three-module, 90-hour micro-certificate prepared participants for entry-level roles in CNC programming.

CNC module 1:
Intro to CNC
Participants were introduced to theoretical and practical applications of CNC milling machines used in manufacturing applications. Emphasis was placed on the safe operation and basic understanding of set up and conversational skills.

CNC module 2:
Basic CNC Applications
Participants built on the fundamental applications learned in module 1 with practical, hands-on experience setting up the machine and using advanced conversational programming. Participants became proficient in setting up and using the tooling for a manually written conversational program using previous applications of G and M code.

CNC module 3:
CNC CAD/CAM
Participants received an advanced introduction to CNC using CAD/CAM programming, performing automated programming using Mastercam to create geometry from engineered drawings, and creating toolpaths to produce a completed project.

Hydraulics and Pneumatics
Participants explored fluid power components and circuits. This two-module, 60-hour micro-certificate prepared participants for careers in industrial and manufacturing maintenance, automation building and troubleshooting, mobile equipment troubleshooting and repair, construction equipment troubleshooting and repair, and entry-level fluid power specialist.

Hydraulics/Pneumatics module 1:
Components, Circuits and Systems
Participants learned about fundamental fluid mechanics, including the application of fluid power components and systems in industrial and mobile machinery and equipment.

Hydraulics/Pneumatics module 2:
Components, Circuits and Systems
Participants expanded knowledge of fundamental fluid mechanics and the application of fluid power components and systems in industrial and mobile machinery and equipment.

Industrial Automation
Participants explored the fundamentals of modern automation. This three-module, 96-hour micro-certificate prepared participants for careers in manufacturing and industrial maintenance, automation technicians, PLC programming, and machine building and integration. Employees working as manufacturing supervisors and lead hands benefitted from training in automation technology.

Industrial Automation module 1:
Fundamentals
Participants learned the fundamentals of pneumatic and electro pneumatic controls, including industrial sensors, control valves, and pneumatic cylinders. Participants began with the make up and operating characteristics of control circuit components, followed by the design and troubleshooting of control circuits. Lab exercises provided hands-on experience with design, production and troubleshooting.

Industrial Automation module 2:
PLC Programming
Participants expanded their knowledge of industrial inputs and outputs, learning functional design, hardware configuration, programming, and Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) application. Labs incorporated design and programming of PLC control circuits, using industrial applications as examples. Participants used PLC programming software to create their programs and test their control designs.
Industrial Automation module 3:
Advanced Controls and Integration
Progressing from Automation 2, participants increased their knowledge of PLCs by learning new hardware and programming tools. Participants learned how a PLC interconnects with other PLCs to control large automation lines, how it interacts with industrial robots, as well as how complex input and output analog devices are used in controls design.

Robotics
Participants explored industrial robotic motion, control and troubleshooting. This three-module, 96-hour micro-certificate prepared participants for careers in robot programming, machine-building and integration, manufacturing maintenance, and automation technician.

Robotics module 1:
Safety and Fundamentals
Modern industrial robots are complex, integrated systems with electrical, electronic, mechanical and software aspects. Participants learned basic robotic programming, mechanical design of industrial robots, and tools used for applications such as gripping, welding and painting. Participants used simulation software and hands-on programming to learn, with safety emphasized throughout the course.

Robotics module 2:
Advanced Programming
Participants covered advanced programming and hardware concepts associated with industrial robots. They also programmed multiple robots to work together and with other automation systems, increasing efficiency and throughput of industrial automation processes. Participants furthered their understanding of robot safety procedures and program organization by creating safety zones, subroutines and macros.
Robotics module 3:
Integration and Applications
Participants learned about other types of industry robots, including cooperative robots and pick and place robots. Labs taught students to design programs for and troubleshoot these robots. Participants learned how robots and PLCs integrate together and with manufacturing facilities, as well as how to justify the cost of automating a process.

Quality Management
In this two-module, 40-hour micro-certificate, participants built a foundation in quality management theories and methodologies and learn tools and techniques for a systematic approach to problem solving and root cause analysis. Participants also developed project management and change management soft skills to support their quality management skillset.

Quality Management module 1:
Fundamentals of Quality Management
This module focused on theories and methodologies that provide a foundation of the history and core principles of quality management. Topics included an introduction to quality, Total Quality Management, and an overview of Six Sigma and Kaizen.

Quality Management module 2:
Tools and Techniques
This module focused on tools and techniques that may be applied in the manufacturing and other service industries. Topics included problem solving, continuous improvement and an introduction to value stream mapping. Students explored tools such as fishbone diagram, PDCA, 5 Whys, and Pareto charts. Participants had the opportunity to apply these tools and techniques to case studies and in teamwork activities. They also developed project management and change management soft skills.

Leadership in Manufacturing
In this five-module, 30-hour micro-certificate, participants built a solid foundation and broad business knowledge base of management, with a focus in manufacturing. Participants developed both operational management and leadership skills while learning to motivate, inspire and lead their teams to success.

Leadership in Manufacturing module 1:
Start Your Engine
Managers and leaders have a significant impact on organizational success. In this module, students discussed the importance of a manager’s leadership styles, attitudes, behaviours, and skills, and explored the role of a manager/leader in relation to individuals, groups, and the organization as a whole.

Leadership in Manufacturing module 2:
Communication
Managers require effective communication skills in one-on-one interactions and meetings in order to develop good working relationships and maintain a spirit of rapport and teamwork. In this module, students learned how to improve relationships at work through the use of voice dynamics and body language, and by learning to listen, question, and give feedback effectively.

Leadership in Manufacturing module 3:
Quality Team Development
In this module, students learned how to create and maintain a successful team. They explored the stages of team development, effective team behaviours, and the role of the leader in order to set team goals and develop strategies for managing conflict within a team.

Leadership in Manufacturing module 4:
Performance Coaching
Coaching helps companies gain and retain top talent, increase job satisfaction and improve productivity resulting in increased profits. In this module, students examined the coaching model, and learned to apply its principles to maximize employee performance and foster employee commitment, satisfaction and dedication.

Leadership in Manufacturing module 5:
Change Management
Managing change is a critical skill for any leader. In this module, students learned theories, models, strategies and processes to help leaders provide individuals and organizations with the awareness, motivation, knowledge and ability to change.

The hydraulics training course provided by the RapidSkills project has been one of the best training courses, if not the best training course, I’ve had the honour of participating in. Attending training during a pandemic can certainly be a challenge, but RapidSkills and the instructor of the course made the most of it and gave us updates promptly to any potential changes happening. The instructor was very knowledgeable, blended hands-on learning and theory together in a manner that made the material fun and easy to learn. I highly recommend RapidSkills to anyone looking to advance knowledge or training in their respective industry.—John Fiebrich, Mechanical Designer, Weldco-Beales Manufacturing
Success stories
In this video, learn how the RapidSkills micro-credentials program helped employees at Napoleon and Kumi Canada Corporation advance their careers.
In this video, hear how Prodomax Automation Ltd. improved and developed the skillsets of its employees with the RapidSkills micro-credentials program.
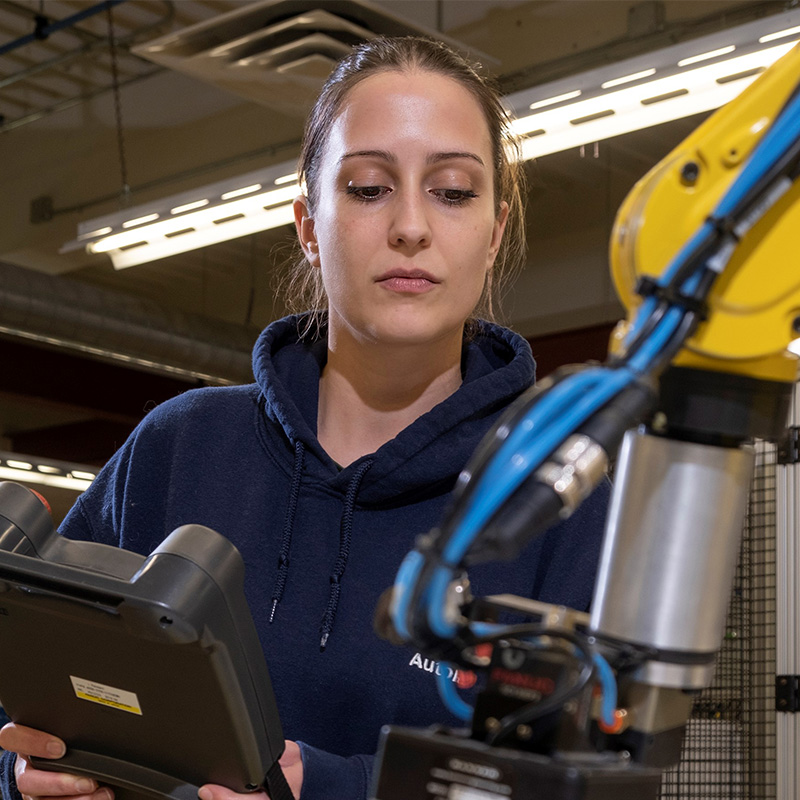

I was very interested in the RapidSkills program because it’s so practical and offers many hands-on opportunities. The hybrid format of the robotics course was perfect— I could get the best of both worlds and still be able to work part-time at my job with Autoliv. It was great to use the machines and work collaboratively with my classmates on different projects, as well as learn theoretical ideas from home. This course has opened my eyes to so many things that will help me grow personally and professionally.—Rachel Smith, past RapidSkills participant
Featured partners
The RapidSkills program has worked with employers from the auto and advanced manufacturing sectors across Simcoe County, including:

Canplas Industries Ltd. has been a leader in the construction plastics industry since 1966.
From the very beginning, our dedicated team of employees prioritized an unrelenting commitment to customer service, focusing on safety, stringent quality and continuous improvement.
Innovation is part of our DNA, with new product solutions being developed and introduced for all of our market segments which include plumbing, ventilation, separation technologies and central vacuum.

CSR is a proven leader in formulating, manufacturing, and filling of personal care and colour cosmetic products.
For over 65 years, we have helped build successful consumer brands for some of the industry’s most reputable companies. Our focus on consistency, performance and reliability in the context of strict current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) guidelines. This makes CSR the right choice for North American and international companies looking for a complete range of product innovation, manufacturing and filling solutions.

The Electric Motor Coil Company (EMCC) is a proven industry-leading supplier of motor coils, generator coils, commutators and slip rings.
Our products are sold to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and aftermarket winding and motor repair customers worldwide. EMCC operates out of a 40,000-square foot-state-of-the-art factory with a fully equipped testing laboratory on site. EMCC has automotive industry-type strengths, including low-cost coil manufacturing, labour efficiency models, and automated processes.
We have a highly skilled and experienced workforce combined with a proven manufacturing methodology – designed to reduce cost, raise quality, and ensure on-time delivery. Our extensive capabilities span a large variety of applications. We are committed to finishing every project on time, on budget, and to the highest standards of quality. We offer the responsive services that you would expect from a world-class coil supplier.

Innovative Automation designs and builds industrial automation equipment, mostly for the automotive industry.
We don’t design and build the parts that go into a vehicle; we design and build the systems that produce the parts.

Kumi Canada Corporation (KCC) is a plastic injection molding company. The company was established in January 1997 by Kumi Kasei Co., Ltd., of Japan and Kamco Industries Inc., of Ohio, to supply automotive parts to Honda of Canada and other related manufacturers in Canada.
Our success in this highly competitive industry depends on the efforts of our associates to work together as a team to provide the highest quality products to our customers.

Molded Precision Components (MPC) was established in 1980 to address the automotive industry need for a responsive prototype molding shop, specializing in high-quality plastic parts such as gears and complex assemblies.
Today, that legacy remains strong, but under new ownership since 2006, MPC has developed its capabilities and technologies far beyond prototyping.
Leading our sector in Industry 4.0 implementation, MPC offers a full-service, multi-disciplinary engineering, product development and precision injection molding service, complemented with our own in-house tool-building operation.

MTH Manufacturing Inc. is located in Elmvale, ON, just 70 minutes north of Toronto and two hours from the United States (U.S.) border.
Established in 2007, MTH Manufacturing Inc. specializes in machining and assembly of commercial vehicle components in a lean production environment.
Our manufacturing capabilities are enhanced by our ability to design and develop products and processes, both to optimize production processes and to improve product designs. Our approach includes using ISO 9001 based business systems as well Six Sigma improvement tools.

For more than 50 years, Prodomax has built a reputation as a specialized industrial engineering firm focused on turnkey integration of complex manufacturing production systems for automotive companies which produce structural underbody components.
We engineer and deliver automation solutions that advance your competitive edge, integrating assembly, welding and material handling, including both laser-cutting and laser-welding technologies.

Raytheon ELCAN is a Canadian optics innovation centre with over 70 years’ experience in Midland, ON.
ELCAN is a strategic partner for our global customers. We design and manufacture high-precision opto-mechanical/opto-electronic systems to help our customers see farther and faster across air, land, sea and space domains.
Proud to support our local, national and global communities, Raytheon ELCAN strives to deliver a world-class employee experience where our employees can work, grow and belong.

SAE is a North American best-in-class manufacturer that specializes in solutions for electrical grounding, alternating current (AC) mitigation, and cathodic protection.
SAE’s innovative design techniques and product technologies, combined with the leading-edge expert knowledge and extensive field experience, help get you what you need for reliable grounding and safety protocols.
SAE’s grounding products and electrodes are designed for high performance, extremely long lifetimes, maintenance-free reliable operations, and are inherently resistant to theft.
SAE further specializes in engineering design that integrates site geography, soil characteristics and soil resistivity data with advanced computer modeling tools to ensure our clients’ electrical protection and ambient noise mitigation specifications are met or exceeded.

Weldco-Beales Mfg. (WBM) designs and manufactures specialized heavy equipment attachments for OEM’s dedicated to servicing the construction, forestry, mining, scrap recycling, road maintenance and resource industries. Typical attachments include buckets, blades and plows, forks, grapples, tire handlers, cable reelers, ejector bodies, guarding structures and custom products.
Our focus is customer success, based on honesty, fairness and our commitment to quality. Collaboration and problem-solving are supported by full engineering capabilities and our wealth of industry experience.
WBM is 100 per cent Canadian owned and has operated since 1945 in Canada, committed to continual growth and exploration of opportunities that capitalize on our strengths to serve the global market.

After moving to Ontario, I needed working knowledge of industrial automation and manufacturing to find employment. While taking this course, I was able to prove key concepts to my current employer which resulted in them hiring me.—Alex Lambrecht, Maintenance Electrician
Featured faculty
Brent Belford has taught at Georgian for 17 years. He is also the academic technologist for the Mechanical Technician – Precision Skills program. He has been a licensed mechanic for over 25 years where he worked largely on performance and custom builds. Brent’s machining skills were used for the manufacturing of performance and racing parts. He’s still involved with racing.
Adam Bowman has over 20 years of experience working with robotics and automation. Through occupying various roles such as a new build integrator in advanced manufacturing and now as a college professor and corporate trainer, Adam brings a wealth of knowledge and diverse experience. He enjoys working with students and industrial partners to help meet their learning needs and provide companies the opportunity to keep pace with the ever-changing technology landscape.
A passionate people leader with 18 years’ experience, driving sales, marketing, and operations teams to success through coaching. Peter Ferreira is highly engaging by using motivational, inspirational and supportive techniques. He is known for leading by example in various industries, including Software as a Servive (SaaS), technology, ecommerce, educational technology (EdTech), retail, wholesale and financial. Peter is a true professional who loves to share best practices, and spark discussion and collaboration to foster learning through the art of corporate training.
Gary Harris has been a full-time teacher with Georgian for 18 years. He is a mould maker by trade and has travelled the world teaching and sharing his passion for design and manufacturing. Gary developed the Precision Machining micro-certificate in response to the needs of the local automotive and advanced manufacturing sectors.
Phil LeBoeuf has worked in the skilled trades field since 1977. A licensed industrial millwright, Phil has worked in various manufacturing industries specializing in machine building, plant maintenance and repair, fluid power maintenance and mobile equipment building and maintenance. Phil joined Georgian in 2003 and has become one of the foremost expert skilled trades trainers, having instructed numerous topics related to the trades and workplace safety. His expertise is requested across the province on a number of ministry-regulated initiatives and mandatory training requirements.
Jean-Marc Singh is a driven professional with over 28 years’ experience in project management, engineering, corporate operations, and senior leadership. Jean-Marc has a deep-rooted history within the oil and gas, and manufacturing industries, developing and implementing standard operating procedures (SOPs), quality management systems (QMS), and project management offices (PMOs) for North America, Asia-Pacific (APAC) and Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA). He enjoys working with students and is committed to lifelong learning and professional development.
Contact us
Our team is always available for questions related to corporate training including group rates, custom programming and how to best utilize Georgian resources.
Contact information
Rob Smith
Manager, Continuing Education and Corporate Training
Email Rob
One Georgian Drive
Barrie, ON L4M 3X9
Schedule a consultation
Interested in developing your workforce but not sure where to begin? We’re here to help.
Call 705.722.5149 or have one of our experts contact you to schedule a FREE, no obligation consultation!
Request a quote
Do you have questions about costs or want to discuss your company’s needs with one of our representatives?
Send us an email and let’s connect.
The RapidSkills micro-credentials program was presented by the City of Barrie and Georgian College, in partnership with the County of Simcoe and the Simcoe Muskoka Workforce Development Board. This project was funded in part by the Government of Canada and the Government of Ontario.